What Popular 3D Printing Technology Will You Use in 2019?

FDM vs SLA vs SLS
So you’ve finally decided that you are going to get a 3D printer. You are ready to bring your ideas to life, creating your own little real-world gaming figures, building objects for around the home, or prototyping your latest invention. However, you’re stuck. What type of 3D printer should you be using?
You have for sure taken the steps to research the best 3D printers for beginners, however picking the type of 3D printer that you will use intersects at what you will be using the 3D printer for, and your overall budget.
Currently, on the market, there are three popular printing technologies FDM vs SLA vs SLS (Fused Deposition Modeling, Stereolithography, & Selective Laser Sintering). Today you are going to learn all about these technologies and how they can apply to you.
A Quick Refresher
3D printing nowadays has a bigger reach of topics and uses across industries than one may think. From major corporations to small start-ups, to the at-home hobbyist, 3D printing is used to take on a host of challenges in design, manufacturing, and engineering.
In short, 3D printing allows users to create a solid, and at times functional objects from a computer aided design file. Though still a relatively new technology, the latest 3D printers are a fraction of a cost of what they were years ago, allowing anyone with some spare change to join in on the fun.
Nevertheless, when considering what you will be printing, it is very important that you weigh the options of an FDM, SLA and SLS printer. Some of these technologies are more tailored toward those looking to build a business, while others are great if you want something for your desktop at home.
Here is everything you need to know about FDM, SLA, and SLS printing.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Let’s jump into one of the most common forms of 3D printing and the most user-friendly. Even more so, Fused Deposition Modeling printing is the least expensive option on this list. Chances are that if you have ever seen a 3D printer in person or considered purchasing one it was an FDM printer.
This additive form of manufacturing starts with printing a commonly used printing material like ABS or PLA filament, feeding this printed material through a heated printer nozzle. The material takes a semi-liquid state as it is extruded through this very hot nozzle printing tiny layers of your CAD file, hardening upon contact.
There are countless FDM printers out there, cheaper than ever. Compared to some of the printer technologies on this list there is no post work needed on your print. Basically, come up with an idea and print it.
FDM printers can print a host of strong plastic-like materials, carbon fiber, and even wood, making them great for at home projects and even some prototyping. However, there are some downsides to using an FDM 3D printer.
Not only can FDM printing take a long time, but the “print resolution” or level of detail also cannot really compare to some of the other printing technologies on this list. If you need to create a functional prototype, a highly detailed model etc. FDM printing might not be the best for you.
Recommended 3D Printer
 Source: Ultimaker
Source: Ultimaker
Though there are much cheaper 3D FDM printers out there under $200, the Ultimaker series of printers is unmatched in the FDM printer world, if you want something that is easy to use, reliable, and that is safe. From their extensive community to their host of printing capabilities, Ultimaker is great for a business and your home.
Stereolithography (SLA)
If you have already mastered the world of FDM printing and need to take it to the next level SLA or stereolithography might be right for you. SLA printing uses a very different printing process than its FDM cousin that can generate a host of tremendous quality prints.
Rather than using plastic filament SLA prints use a liquid resin material, SLA printers take your CAD model then emit ultraviolet light into a vat of UV-curable photopolymer. There your print is divided into tiny slices which then emit ultraviolet light into the photopolymer vat.

Source: Formlabs
Each layer is then hardened creating a solid layer. After the print is completed it undergoes a chemical bath to remove the excess resin, then placed in UV light for hardening.
The laser technology used to create the prints will have you creating some of the most accurate and high-resolution prints that you have ever seen, making it perfect for model builders and designers. SLA printing is also much faster than FDM or SLS printing.
Yet, there are some downsides to printing using an SLA printer. Aside from the huge jump in price, SLA printers tend to print in a much smaller volume compared to FDM printers and even some SLS printers, and you will be fairly limited on the type of material you can use.
Even more so, SLA printers need to be handled with care as the resin used to create your hi-def prints is very toxic and not recommended for inexperienced users. Yet if you can overlook these small caveats, SLA printing has the most appeal on this list for those who want to see tremendous detail in their life. SLA printing is great for business and enthusiasts.
Recommended 3D Printer
 Source: Formlabs
Source: Formlabs
Formlabs is the place to go if you are looking for an SLA printer. As one of the first companies to get in the consumer SLA printing game, their printers consistently make it on the top of everyone’s list for being consistent, high quality, and designed very well. You can even 3D print ceramic.
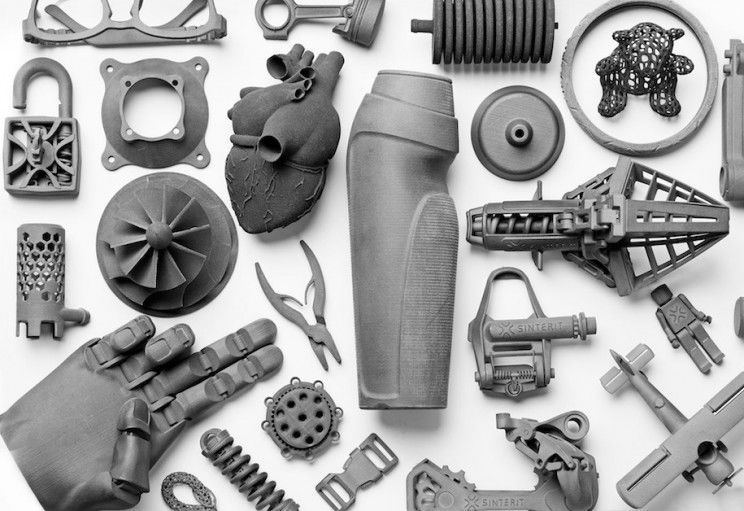
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
 Source: Sinterit
Source: Sinterit
If you are looking to build products, test models, and appreciate unmatched levels of detail on your prints, then SLS printing is the way to go. However, you should be warned the ecosystem, as well as the technology needed to create SLS printing, is expensive, sometimes jumping as high as $15,000.
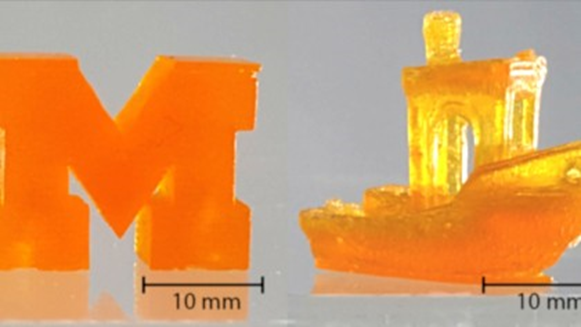
New 3D Printer Prints 100 Times Faster Than Standard Printers
However, you get what you pay for as the technology here is impressive and an excellent choice for industrial design companies. SLS works by using a laser to melt and fuse powdered raw materials to form a single solid object.
Basically, the powder used for printing in this method can be made of a variety of materials, including silicates, polystyrene, or even metal. SLS printers are the kings of detail, however, their benefits do not stop there.
SLS prints are durable and even fully functional fresh out of the printer, allowing users to print working parts and even a flip book if needed. Though post-production work is required for these prints, users get a print that is ready for use.
Recommended 3D Printer
 Source: Sinterit
Source: Sinterit
SLS printing would have set you back a few hundred thousand dollars years ago, but now you can get one for your workshop desktop. Sinterit is the place to go if you are on the market for an SLS printer. Their printers are both reliable and intuitive for those looking into this 3D printing technology.
